What type of vaccine involves host synthesis of viral antigens? This intriguing concept sets the stage for an exploration into the innovative realm of vaccine development. Host synthesis of viral antigens offers a promising avenue for the creation of vaccines that harness the body’s natural immune mechanisms to combat viral infections.
By delving into the intricacies of this technique, we will uncover the types of vaccines that utilize host synthesis, unravel the mechanisms of action, and examine specific examples of vaccines that have harnessed this technology. Furthermore, we will explore future applications and identify challenges and opportunities in this burgeoning field.
1. Introduction to Host Synthesis of Viral Antigens
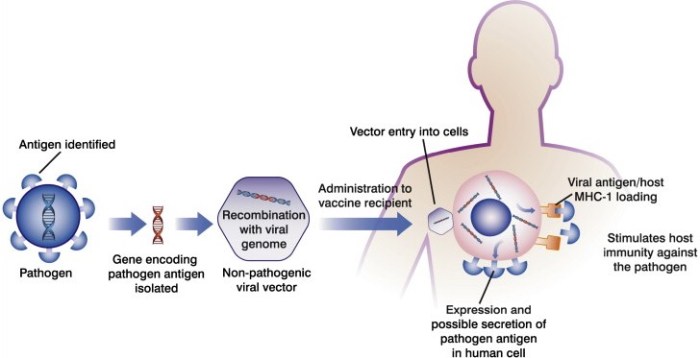
Host synthesis of viral antigens refers to the process where viral antigens are produced within the host’s own cells after vaccination.
The immune system recognizes and responds to viral antigens, which are molecules that are unique to the virus. When the immune system encounters a viral antigen, it produces antibodies and activates other immune cells to fight the infection.
Using host synthesis of viral antigens in vaccine development offers several advantages, including the ability to induce both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses, as well as the potential for rapid production and scalability.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using this approach, such as the potential for insertional mutagenesis and the need for careful optimization of the vaccine design to ensure safety and efficacy.
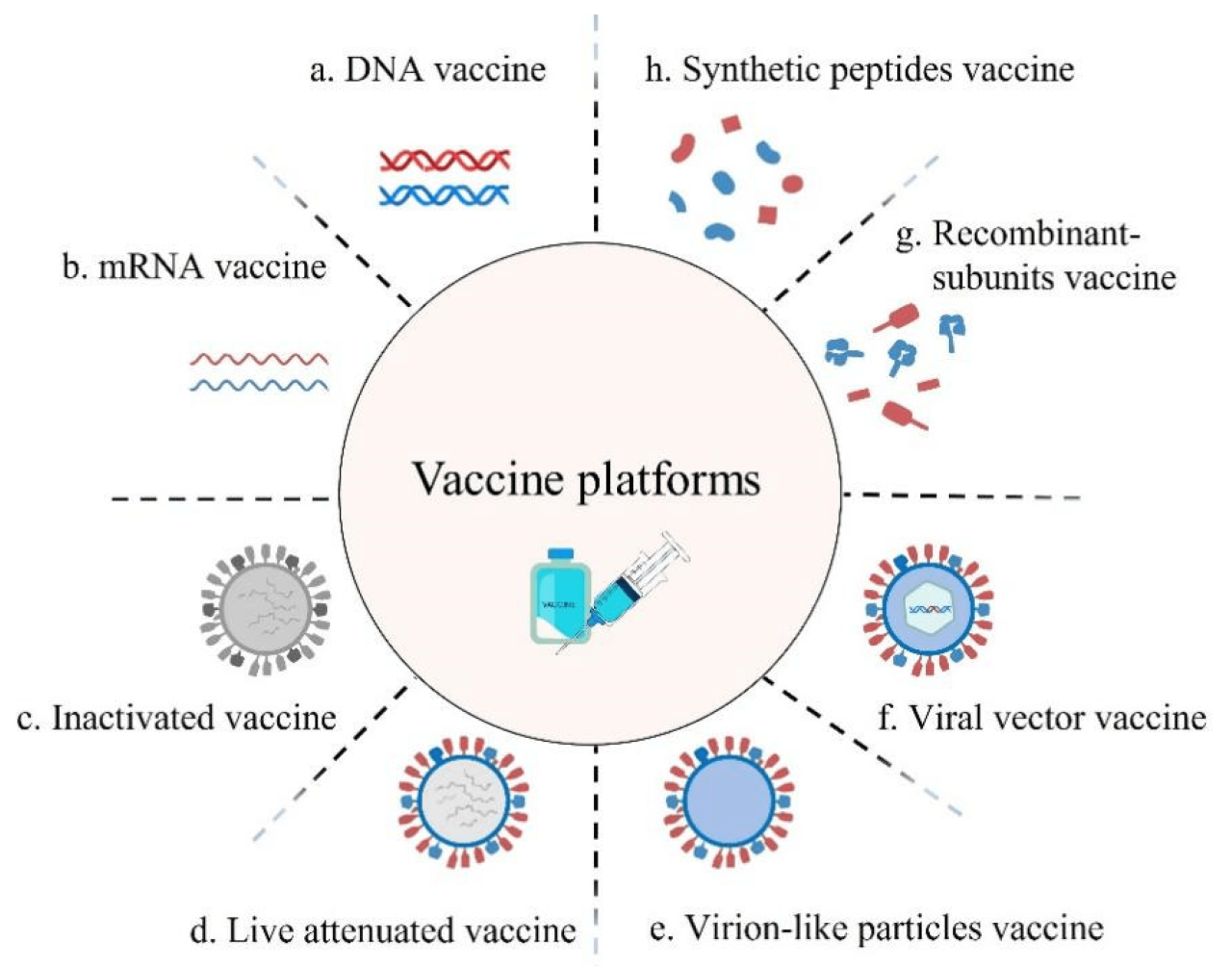
2. Types of Vaccines that Utilize Host Synthesis of Viral Antigens
DNA vaccines
DNA vaccines contain a plasmid DNA that encodes the gene for the viral antigen. When the DNA is injected into the host, it is taken up by cells and transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated into the viral antigen.
mRNA vaccines
mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that encodes the gene for the viral antigen. When the mRNA is injected into the host, it is translated into the viral antigen without the need for transcription.
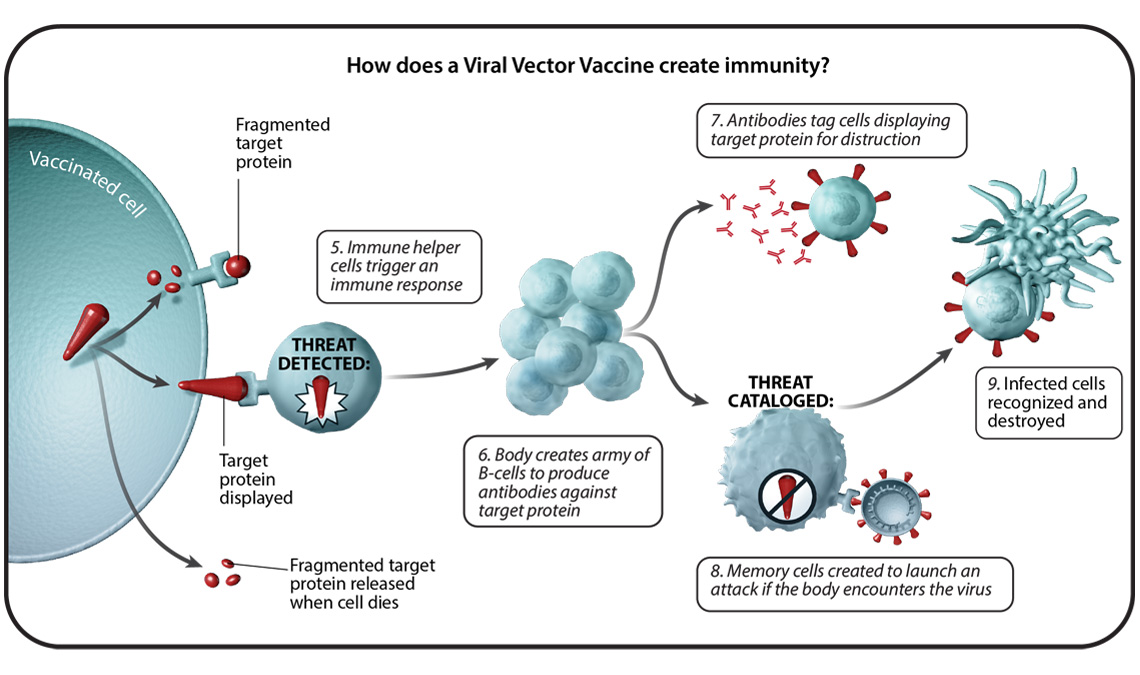
Viral vector vaccines, What type of vaccine involves host synthesis of viral antigens
Viral vector vaccines use a modified virus to deliver the gene for the viral antigen into the host’s cells. The modified virus is engineered to be non-replicating, so it cannot cause disease, but it can still deliver the gene for the viral antigen to the host’s cells.
3. Mechanisms of Action for Host Synthesis of Viral Antigens
Host synthesis of viral antigens occurs when the gene for the viral antigen is delivered into the host’s cells. The gene is then transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated into the viral antigen.
The viral antigen is then presented on the surface of the host’s cells, where it can be recognized by the immune system. The immune system then produces antibodies and activates other immune cells to fight the infection.
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) play a critical role in the immune response to host-synthesized viral antigens. APCs are cells that capture and present antigens to the immune system. When an APC encounters a host-synthesized viral antigen, it will capture the antigen and present it on its surface.
The immune effector cells that are responsible for fighting the infection are primarily T cells and B cells. T cells are responsible for cell-mediated immunity, which involves killing infected cells. B cells are responsible for humoral immunity, which involves producing antibodies.
4. Examples of Vaccines that Use Host Synthesis of Viral Antigens: What Type Of Vaccine Involves Host Synthesis Of Viral Antigens
DNA vaccines
One example of a DNA vaccine that uses host synthesis of viral antigens is the HPV vaccine, which protects against human papillomavirus (HPV).
mRNA vaccines
One example of an mRNA vaccine that uses host synthesis of viral antigens is the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, which protects against COVID-19.
Viral vector vaccines, What type of vaccine involves host synthesis of viral antigens
One example of a viral vector vaccine that uses host synthesis of viral antigens is the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine, which protects against COVID-19.
5. Future Directions and Applications of Host Synthesis of Viral Antigens
Host synthesis of viral antigens is a promising approach for vaccine development, and there are several potential future applications for this technology.
One potential application is the development of vaccines against emerging or pandemic diseases. Because host synthesis of viral antigens can be used to rapidly produce vaccines, it could be a valuable tool for combating new and emerging diseases.
Another potential application is the development of vaccines that are more effective against variants of viruses. Host synthesis of viral antigens could be used to produce vaccines that are tailored to specific variants of viruses, which could improve their effectiveness.
There are still some challenges that need to be overcome before host synthesis of viral antigens can be widely used for vaccine development. These challenges include the need for careful optimization of the vaccine design to ensure safety and efficacy, as well as the need for more research on the long-term effects of this approach.
Questions Often Asked
What are the advantages of using host synthesis of viral antigens in vaccine development?
Host synthesis of viral antigens offers several advantages, including the ability to induce both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses, the potential for rapid production, and the flexibility to target specific viral proteins.
What are some examples of vaccines that utilize host synthesis of viral antigens?
Examples of vaccines that utilize host synthesis of viral antigens include DNA vaccines, mRNA vaccines, and viral vector vaccines. These vaccines have shown promising results in clinical trials against various viral diseases.