As enzyme in fat breakdown crossword clue takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world of enzymatic wonders, where the intricate process of fat metabolism unfolds. Enzymes, the masterminds behind countless biological reactions, play a pivotal role in breaking down fats, providing the body with essential energy and paving the way for a deeper understanding of metabolic pathways.
Delving into the specific enzyme responsible for fat breakdown, we unravel its unique structure, optimal conditions for activity, and the intricate mechanisms that regulate its function. This exploration illuminates the enzyme’s role in maintaining metabolic balance and highlights its clinical significance in diagnosing and treating fat metabolism disorders.
Enzyme in Fat Breakdown: Definition and Role
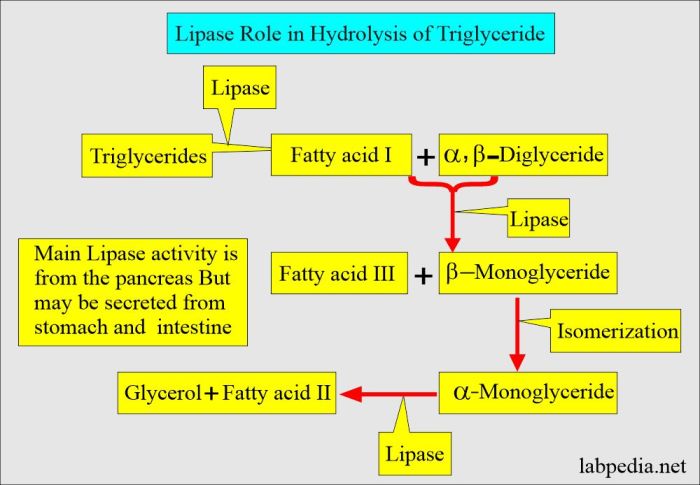
Enzymes are protein molecules that act as catalysts in biological reactions, facilitating chemical transformations without being consumed themselves. In fat breakdown, a specific enzyme plays a crucial role in the hydrolysis of triglycerides, the main component of fats. This enzyme, known as lipase, breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol.
Mechanism of Fat Breakdown by Lipase
Lipase catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides by cleaving the ester bonds that link the fatty acids to the glycerol backbone. This reaction occurs in a stepwise manner, with the release of one fatty acid at a time. The resulting fatty acids and glycerol can then be further metabolized for energy production or storage.
Characteristics of Lipase
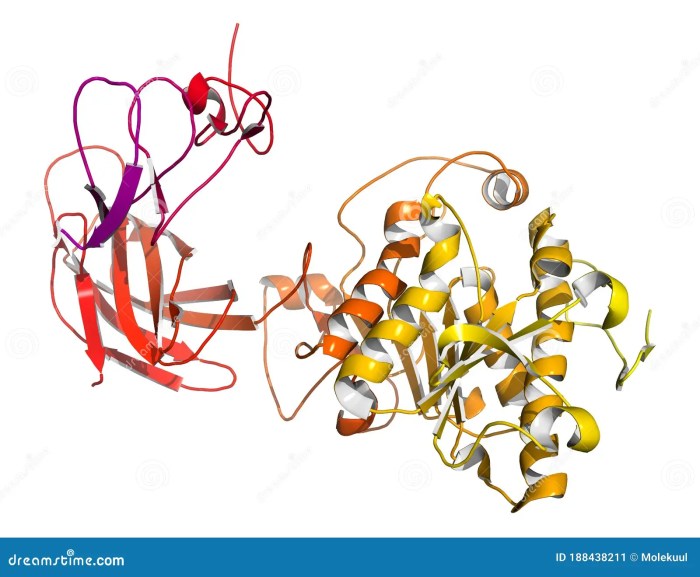
Chemical Structure and Composition
Lipases are typically composed of a single polypeptide chain with a molecular weight ranging from 20 to 60 kDa. They contain a catalytic triad consisting of serine, histidine, and aspartate residues, which are essential for enzyme activity.
Optimal pH and Temperature
The optimal pH for lipase activity varies depending on the specific enzyme, but it generally ranges from 7.0 to 8.5. The optimal temperature for activity is also enzyme-specific, but it typically falls within the range of 30-40°C.
Factors Affecting Stability and Activity
The stability and activity of lipase can be affected by various factors, including pH, temperature, ionic strength, and the presence of inhibitors or activators. Extreme pH or temperature conditions can denature the enzyme, reducing its activity. Inhibitors, such as detergents or heavy metals, can bind to the enzyme and block its catalytic site, while activators can enhance enzyme activity by facilitating substrate binding or stabilizing the enzyme structure.
Regulation of Lipase Activity
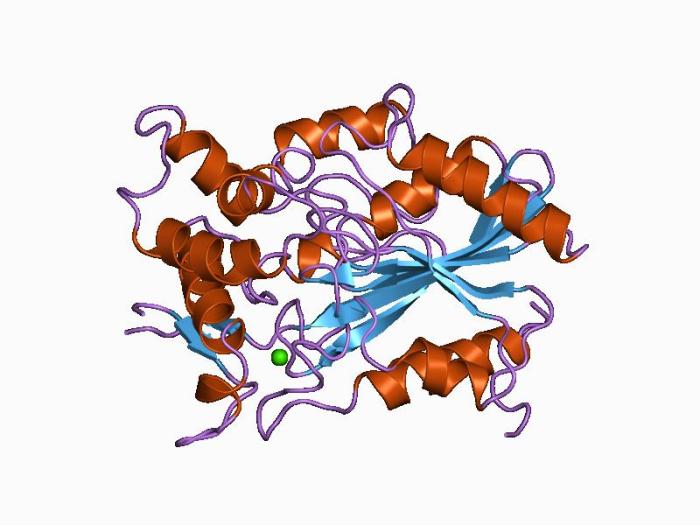
Cofactors and Inhibitors
Lipase activity is regulated by various mechanisms, including the presence of cofactors and inhibitors. Cofactors, such as calcium ions, are essential for enzyme activity, while inhibitors, such as bile salts, can modulate enzyme activity by competing with substrates for binding to the catalytic site.
Hormonal Regulation
Lipase activity is also regulated by hormones. For example, the hormone glucagon stimulates lipase activity in adipose tissue, promoting the release of fatty acids into the bloodstream for energy production.
Clinical Significance
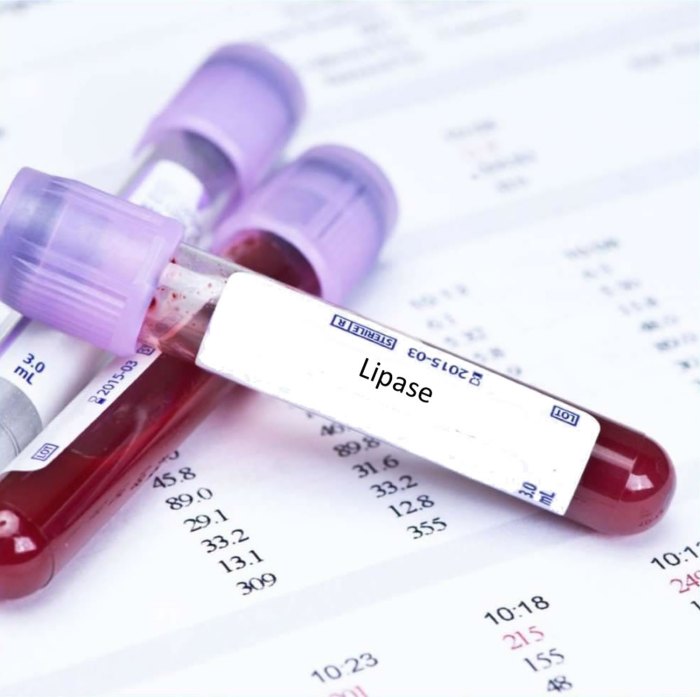
Lipase Deficiency or Malfunction, Enzyme in fat breakdown crossword clue
Deficiency or malfunction of lipase can lead to impaired fat digestion and absorption, resulting in conditions such as steatorrhea, where undigested fats are excreted in the feces. This can lead to malnutrition and weight loss.
Diagnostic Tests
Lipase levels can be measured in blood tests to assess pancreatic function and diagnose conditions such as pancreatitis. Elevated lipase levels may indicate inflammation or damage to the pancreas.
Therapeutic Interventions
Therapeutic interventions targeting lipase can include enzyme replacement therapy for lipase deficiency and the use of lipase inhibitors to treat conditions such as obesity and hyperlipidemia.
FAQ: Enzyme In Fat Breakdown Crossword Clue
What is the primary function of the enzyme involved in fat breakdown?
The enzyme responsible for fat breakdown plays a crucial role in hydrolyzing triglycerides, the primary components of fats, into fatty acids and glycerol.
How does the optimal pH and temperature affect the activity of the enzyme?
The enzyme exhibits optimal activity within a specific pH range and temperature, ensuring efficient fat breakdown under physiological conditions.
What factors can influence the stability and activity of the enzyme?
Various factors, including pH, temperature, and the presence of inhibitors or cofactors, can impact the stability and activity of the enzyme.