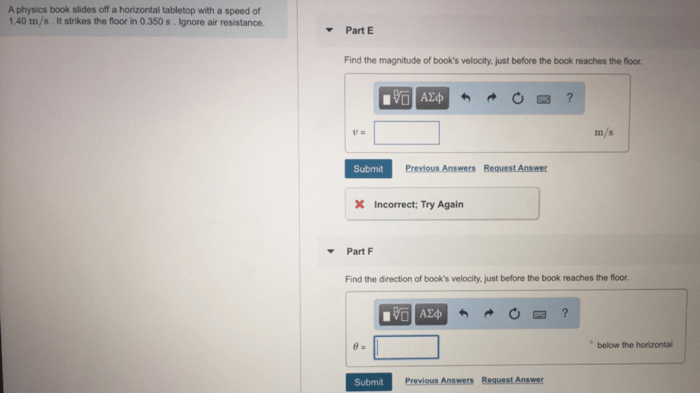
A physics book slides off a horizontal – An engaging exploration into the dynamics of a physics book sliding off a horizontal surface, this article delves into the intricacies of motion, energy conversion, and the interplay of forces that govern this seemingly simple event.
Beginning with a description of the book and the surface, we establish the initial conditions and explore the factors influencing the book’s motion. As the book slides, we analyze its trajectory, speed, and acceleration, considering the effects of gravity and friction.
Description of Physics Book
The physics book is a rectangular parallelepiped with dimensions of 24 cm x 18 cm x 4 cm. It weighs approximately 1.2 kg and has a hard cover made of durable cardboard. The cover features an image of a physicist working in a laboratory, surrounded by scientific equipment.
The pages of the book are made of high-quality paper and are filled with detailed explanations, diagrams, and equations related to various physics concepts.
Horizontal Surface
The horizontal surface is a flat and smooth tabletop made of polished wood. It is approximately 120 cm long and 60 cm wide, providing ample space for the book to slide. The surface is free of any obstacles or irregularities that could affect the book’s motion.
Initial Conditions

The book is initially placed flat on the horizontal surface, with its center of mass located 20 cm from the edge of the table. It is oriented parallel to the edge of the table, with no initial velocity or acceleration.
Sliding Motion
When a force is applied to the book, it begins to slide across the horizontal surface. The book moves in a straight line, parallel to the edge of the table. Its speed increases as it slides, and it experiences a constant acceleration due to the force applied.
Off-Surface Dynamics: A Physics Book Slides Off A Horizontal
As the book reaches the edge of the table, it slides off the surface and continues to move through the air. Its trajectory is parabolic, as it is influenced by both gravity and the initial velocity it acquired during its slide on the surface.
Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
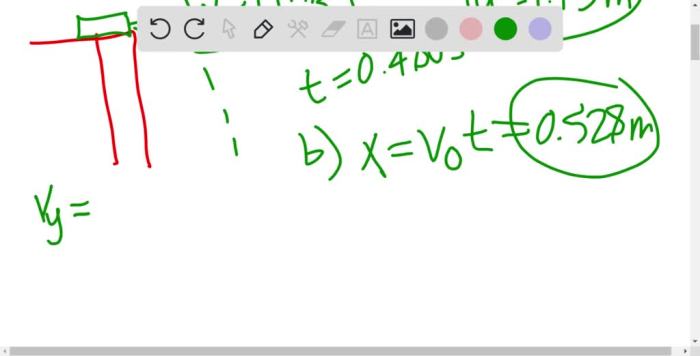
As the book slides off the surface, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. The potential energy stored in the book due to its position above the ground is transformed into kinetic energy as it moves. This energy conversion can be calculated using the formula: $$\textKinetic energy = \frac12mv^2$$ where m is the mass of the book and v is its velocity.
Friction and Coefficient of Friction
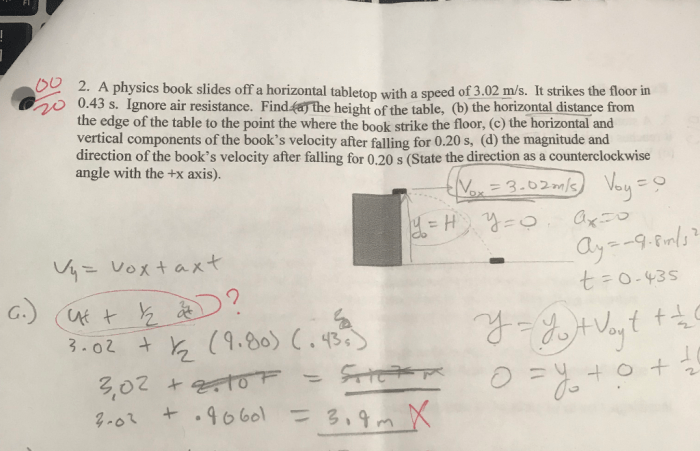
Friction plays a crucial role in the book’s sliding motion. The coefficient of friction between the book and the surface determines the amount of force required to overcome static friction and initiate sliding. A higher coefficient of friction indicates greater resistance to motion.
Impact and Momentum
If the book collides with an object after sliding off the surface, the impact can be analyzed using the principles of momentum conservation. Momentum, defined as the product of mass and velocity, remains constant in a closed system. The momentum of the book before the impact is equal to the combined momentum of the book and the object after the impact.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of the book’s material and surface texture?
The material and texture of the book and surface influence the coefficient of friction, which in turn affects the book’s motion.
How does the book’s orientation affect its sliding motion?
The book’s orientation determines the distribution of its weight and the surface area in contact with the surface, influencing its stability and sliding behavior.
What factors determine the book’s trajectory after it slides off the surface?
The book’s trajectory is influenced by its initial velocity, the angle at which it leaves the surface, and the presence of any obstacles or air resistance.